上一篇文章中我們簡單的理解完 LangChain 以後,接下來我們要來談談 LangGraph,某些方面它真的救了一把 LangChain 的名聲。
LangGraph 大約是在 2024.02 時推出的,它那時主要是為了解決 LangChain 被罵很久的不足,以下是官網的說明 :
https://docs.langchain.com/oss/javascript/langchain/philosophy
February 2024: LangGraph is released as an open source library. If you recall, the original LangChain had two focuses: LLM abstractions, and high level interfaces for getting started with common applications. What was missing was a low-level orchestration layer allowing developers to control the exact flow of their agent. LangGraph was exactly that. LangGraph also learned from lessons in LangChain and built functionality we discovered was needed in LangChain: streaming, durable execution, short term memory, human-in-the-loop, and more.
其中重點是 What was missing was a low-level orchestration layer allowing developers to control the exact flow of their agent 這句話。
簡單的說就是如果你本來要在 LangChain 要控制 Agent 的流程,然後做到一些比較複雜的流程情境會很困難,或是說做不到,因此才會有 LangGraph 這個東西跑出來。
然後我自已覺得從這份就可以知道它想做到什麼,然後我自已是歸類為 :
🤔 Agentic AI 與 AI Agent 的差別 ?
當初我看到這名詞時第一個問題就是,這鬼東西和 AI Agent 是啥關係,還是打錯字嗎 ?
然後下面這張圖是我從這篇論文上看到的,我自已覺得蠻好懂的,讓我理解了這兩個差別。
AI Agents vs. Agentic AI: A Conceptual Taxonomy, Applications and Challenges
在最開始的時後,咱們的 AI Agent 就是可以自行觀察、思考、然後再行動,但是如果接下來的任務開始變的複雜,例如需要與其它的 AI Agent 合作,然後它們都需要分享記憶,並且要做的事情可能根據很多不同的情境,會有不同的分支,其中還包含可能需要人工判斷的,那這種情況下 AI Agent 就顯的有點做不到了。
因為才會提到Agentic AI這個概念,而 LangGraph 就是為了要做這個而產生的。
順到說一下這也是之前 LangChain 被罵沒有彈性與問題的其中一個原因,很難做到這種 Agentic AI。
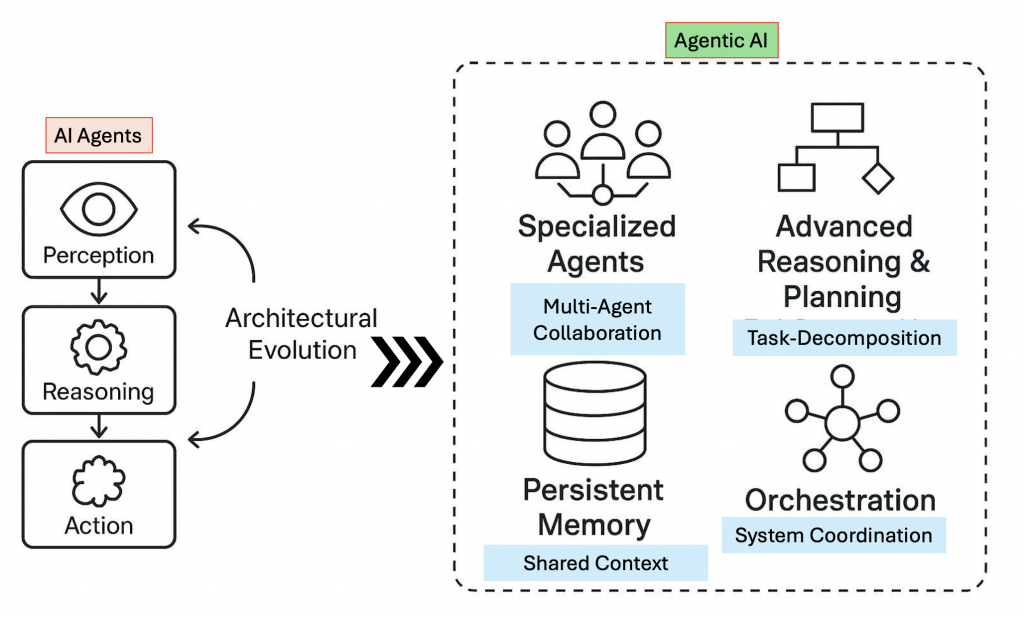
圖片來源: AI Agents vs. Agentic AI: A Conceptual Taxonomy, Applications and Challenges
這兩個東西我知道覺得他應該可以說是能做到 Agentic AI 的核心。
這也對應到上圖中的那四個東西,你可以想想應該用這兩個東西就可以完成那些了。
🤔 首先我們來說說 Workflow
它事實上就是一個你這個 Agentic 的 Workflow,也就是工作流,然後它這裡是使用 Graph 的概念來建立出這個 Workflow 如下範例程式碼與圖 :
然後我們這裡的範例就是建立了兩個 mock agent,然後有一個 route,會判斷使用者說的話要交給那個 agent 來處理,然後我們有定義了這整個 workflow 的 state,就是 StateAnnotation,然後就可以讓整個 workflow 都有狀態,這也代表你可以根據前面的人做了什麼事情,來決定你這個 node 要幹啥之類的 ~
import { StateGraph, START, END, Annotation } from "@langchain/langgraph";
const StateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
input: Annotation<string>,
output: Annotation<string>,
});
type State = typeof StateAnnotation.State;
async function WeatherAgent(state: State): Promise<State> {
const question = state.input;
return {
...state,
output: `🌤️ WeatherBot: The weather for "${question}" is sunny 28°C.`,
};
}
async function StockAgent(state: State): Promise<State> {
const question = state.input;
return {
...state,
output: `📈 StockBot: The stock price for "${question}" is $123.45.`,
};
}
function Router(state: State): string {
const question = state.input.toLowerCase();
if (question.includes("weather") || question.includes("天氣")) {
return "weather";
}
if (question.includes("stock") || question.includes("股票")) {
return "stock";
}
return "default";
}
// 建立 graph
const graph = new StateGraph(StateAnnotation) <---------- 重點就是他
.addNode("weather", WeatherAgent)
.addNode("stock", StockAgent)
.addNode("default", async (s: State) => ({
...s,
output: `🤔 Sorry, I can't handle "${s.input}".`,
}))
.addConditionalEdges(START, Router)
.addEdge("weather", END)
.addEdge("stock", END)
.addEdge("default", END);
const app = graph.compile();
const mermaid = app.getGraph().drawMermaid();
console.log(mermaid);
// 測試呼叫
console.log(await app.invoke({ input: "What's the weather today?" }));
console.log(await app.invoke({ input: "Tell me the stock price of AAPL" }));
console.log(await app.invoke({ input: "幫我查天氣" }));
console.log(await app.invoke({ input: "唱歌給我聽" }));
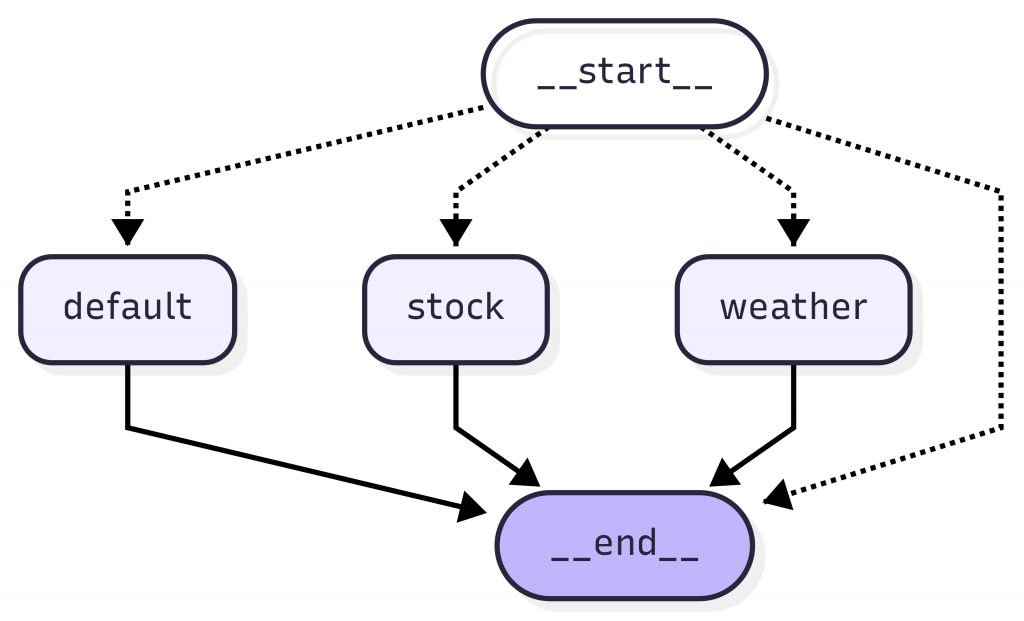
然後你可以用它內部提供的工具產生出 graph 的圖,例如我就用 app.getGraph().drawMermaid() 產生出 mermaid,如下圖,這樣可以讓之後的開發與維護人員看一點就知道這個 workflow 是在做什麼。
🤔 再來我們來說說 State
在上面的程式碼,整個 State 的定義如下 :
const StateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
input: Annotation<string>,
output: Annotation<string>,
});
其中 input 與 output 是我們自已定義的,所以這裡你只要定義好這個 Workflow 所需要的狀態就好。
然後它還有提供一些功能,例如下面的範例可以用 reducer,這個在處理 AI 上下文時會用到。
const State = Annotation.Root({
input: Annotation<number>,
output: Annotation<string[]>({
reducer: (state: string[], update: string[]) => state.concat(update),
default: () => [],
}),
});
然後要注意,它還有很多種方法可以定義 state,例如用 zod 如下範例 :
const StateAnnotation = z.object({
input: z.string(),
output: z.string(),
});
type State = z.infer<typeof StateAnnotation>;
至於要用那個,事實上我有點不確定…… 只知道目前兩個都會 work,再使用上看不出好壞,但目前最新的 1.0.0 官網,看範例都偏多 Zod object,
然後根據官網這段話,感覺…… 應該 Zod object 是主推吧 ?
https://docs.langchain.com/oss/javascript/langgraph/graph-api#schema
The main documented way to specify the schema of a graph is by using Zod schemas. However, we also support using the Annotation API to define the schema of the graph.
從上面程式碼事實上可以知道一件事 :
我們的 Workflow 事實上是在一開始時就定義好的。
🤔 那如果我們要在程式碼執行階段來判斷怎麼辦呢 ?
例如我們在一個 node 中,可能會根據它的處理狀況,產生出要多走 2 條分支的情況,那這時就要用 Send 了。
Send: 動態建立分支(edges),並且允許同時存在多個「分裂 state」版本
簡單的範例就如下,它就可以根據 state.subjects 數量來產生對應數量的路線。
import { Send } from "@langchain/langgraph";
graph.addConditionalEdges("splitNode", (state) => {
// 假設 state.subjects = ["cat", "dog", "fish"]
return state.subjects.map(
(s) => new Send("processSubject", { subject: s })
);
});
然後還有一種情況,如果我們要在 node 中根據某些判斷來走跳到某個 Node 要如何處理呢,那就是用 Command。
Command: 在同一個 node 裡,同時更新 state + 控制流(要去哪個 node)。
import { Command } from "@langchain/langgraph";
graph.addNode("myNode", (state) => {
if (state.foo === "bar") {
return new Command({
update: { foo: "baz" },
goto: "myOtherNode",
});
}
return new Command({
update: { foo: "done" },
goto: "fallbackNode",
});
}, { ends: ["myOtherNode", "fallbackNode"] });
接下來其它的東西基本上就只是往這個上面加,讓這個 Workflow 可以做到更多的事情而已。
🤔 1. Durable execution : 讓 Workflow 能在執行過程中保存狀態,遇到中斷(像是系統錯誤或需要人類介入)時,可以從最後的檢查點繼續,而不用重跑整個流程,這個下一篇會和 LangChain 的 Persistence 一起說說。
Durable execution 有所謂的 Durability Models 也就是說整個 workflow 什麼時後會保存狀態。
這個應該有處理過資料庫的應該有碰過類似的抉擇 ~
🤔 2. human intervention : 就是可以做到工具人問我們事情,等我們回應後,才會執行下一個 Node
下面是官網的範例,真的還算簡單,這個如果要單純用 LangChain 來處理就會比較麻煩點了。
import { interrupt, Command } from "@langchain/langgraph";
const graph = graphBuilder
.addNode("humanNode", (state) => {
const value = interrupt(
// (1)!
{
textToRevise: state.someText, // (2)!
}
);
return {
someText: value, // (3)!
};
})
.addEdge(START, "humanNode")
.compile({ checkpointer }); // (4)!
🤔 3. Streaming : 這個應該已經是標配了
看到現在每個和 LLM 有關的 SDK 或 Framework 都有 Streaming 了。
for await (const chunk of await graph.stream(inputs, {
streamMode: "updates",
})) {
console.log(chunk);
}
🤔 4. Subgraphs : 就很字面上的意思,可以建立子 Graph
這個應該在建立 Multi-Agent 時可以做到,這個我們之後應該會實作到,因為我們可能會有多個 agent 了,然後以下是範例程式碼,也是很簡單。
import { StateGraph, START } from "@langchain/langgraph";
import * as z from "zod";
const State = z.object({
foo: z.string(),
});
// Subgraph
const subgraphBuilder = new StateGraph(State)
.addNode("subgraphNode1", (state) => {
return { foo: "hi! " + state.foo };
})
.addEdge(START, "subgraphNode1");
const subgraph = subgraphBuilder.compile();
// Parent graph
const builder = new StateGraph(State)
.addNode("node1", subgraph)
.addEdge(START, "node1");
const graph = builder.compile();
LangGraph 的整個核心概念事實上真的很簡單,就是 :
Workflow + State
然後裡面各 Node 就可能會有 AI Agent 在工作,所以這也代表一個 Workflow 就可能有多個 AI Agent 在工作,然後他們有個共同 State 會分享整個情報給其它 Agent,讓他們可以合力的一起完成工作。
然後應該也有人有注意到,事實上我今天大部份的範例是都沒有 LLM 的,所以事實上這也代表 :
LangGraph 比較是底層 Workflow 工具
所以如果你是要拿來做 Workflow 我事實上也覺得不是不行。
